A firewall (in Portuguese: Wall of fire) is a computer network device that aims to apply a security policy to a certain point on the network. The firewall can be packet filters, application proxy, etc. Firewalls are usually associated with TCP/IP networks.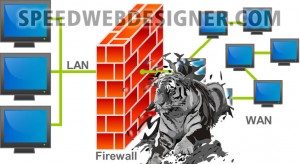
Physical Firewall
Firewalls in the form of hardware (Physical) are specific equipment for this purpose and are most commonly used in business applications. The advantage of using equipment of this type is that the hardware is dedicated rather than sharing resources with other applications. In this way, the firewall may be able to handle more requests and apply filters more quickly.
Firewall systems were born in the late 80's, as a result of the need to create access restriction between existing networks, with security policies in the TCP/IP protocol suite. At this time, the expansion of academic and military networks, which culminated in the formation of the ARPANET and, later, the Internet and the popularization of the first computers, making them easy targets for the incipient hacker community.
Cases of network intrusions and phone system fraud began to emerge, and were portrayed in the 1983 film War Games. In 1988, network administrators identified what became the first major virus infestation. computer and what became known as the Internet Worm. In less than 24 hours, the worm written by Robert T. Morris Jr spread through all the systems of the then existing Internet (formed exclusively by government and educational networks), causing a real “blackout” in the network.
The English term firewall makes a comparative allusion to the function it performs to prevent the spread of harmful accesses within a computer network to a flame-retardant wall, which prevents the spread of fires through the rooms of a building.
Virtual Firewall
With the explosion of electronic commerce, it was realized that even the latest packet filtering technology for TCP/IP might not be as effective as expected. With all the investments made in stateful firewall technology, attacks continued to thrive. Only filtering network packets was no longer sufficient. The attacks began to focus on the specific characteristics (and vulnerabilities) of each application. It was realized that there was a need to develop a new method that could analyze the particularities of each protocol and make decisions that could prevent malicious attacks against a network.
If compared to the traditional model of Firewall — oriented to data networks, the Application Firewall is often installed next to the application platform, acting as a kind of proxy for access to the server (Proxy).
Some open-source projects, such as ModSecurity3 for Apache, IIS and Nginx servers, aim to facilitate the dissemination of the concept to Web applications.
Firewall Cloud (Cloud)
With the knowledge of a diverse community of websites, a new type of security service is born. Online threats range from nuisances like excessive comment and bot spam to malicious attacks like SQL injection and denial of service (DOS) attacks. Cloud systems provide security protection against all these types of threats and more to keep your website safe.
Cloud systems protect all members of a network by identifying attacks on specific sites, so when a new attack starts on a particular site and the security module is triggered, it starts to defend all other sites on the network against the same attack, that is, the cloud system becomes reactive and starts to learn from the attacks that are submitted to a certain network.
Have all this security technology available on your website through SpeedWebdesigner's plans, access Sites Seguro, Click here !